Hồ dynasty
Hồ dynasty
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kingdom of Đại Ngu Đại Ngu Quốc (大虞國) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1400–1407 | |||||||||||
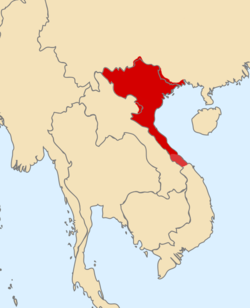 Map of Hồ dynasty in 1401 (Yellow) | |||||||||||
| Status | Kingdom | ||||||||||
| Capital | Tây Đô | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Vietnamese | ||||||||||
| Religion | Buddhism (official), Taoism, Confucianism | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
• 1400–1401 | Hồ Quý Ly (first) | ||||||||||
• 1401–1406 | Hồ Hán Thương (last) | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 1400 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1407 | ||||||||||
| Currency | copper coins, paper money | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Hồ dynasty (Nhà Hồ, 胡朝, Hồ triều) was a short-lived six-year reign of two emperors, Hồ Quý Ly in 1400–01 and his second son, Hồ Hán Thương, who reigned from 1401 to 1406. The practice of bequeathing the throne to a designated son (not simply passing it on to the eldest) was similar to what had happened in the previous Trần dynasty and was meant to avoid sibling rivalry. Hồ Quý Ly's eldest son, Hồ Nguyên Trừng, played his part as the dynasty's military general. In 2011, UNESCO declared the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty in Thanh Hóa Province a world heritage site.[1]
Contents
1 Hồ Quý Ly (c. 1350 – c. 1410)
1.1 Origin and background
1.2 Hồ Quý Ly's ascent to power
1.3 Coup d'etat of Hồ Quý Ly (1399)
1.3.1 Đại Ngu
1.4 Final years
2 Hồ Hán Thương, emperor 1401–06
2.1 Foreign diplomacy
2.2 Defeat and shatter
2.3 Economy and finance
3 See also
4 References
5 Sources
Hồ Quý Ly (c. 1350 – c. 1410)[edit]
Origin and background[edit]
China's province of Zhejiang around the 940s was the origin of the Chinese Hồ/Hú family.[2][3] which was then in the midst of the Five Dynasties struggle. The Hồ claimed descent from the ancient Chinese Emperor Shun. From Zhejiang, the family under Hồ Liêm 胡廉 (Hú Lián in Chinese) migrated south until they established themselves in northern Vietnam. Hồ Liêm, Hồ Quý Ly's great-great-grandfather, moved further south and settled in the province of Thanh Hóa (about 100 km south of the modern city of Hanoi). Some historians bring attention to the fact that Hồ Quý Ly is also known as Lê Quý Ly. In his childhood, Hồ Quý Ly was adopted by Lê Huan after whom he took the family name. He did not change this Lê last name to Hồ until after he had deposed the last king of the Trần dynasty. Because of the short span of the Hồ dynasty and the tragic circumstances he brought upon the country, the family name "Hồ" was disgraced thereafter. However, historians have attributed to Hồ family quite a few notable scholars, dignitaries, and government officials under both the Lý dynasty and Trần dynasty.
Hồ Quý Ly's ascent to power[edit]
The Trần dynasty's authority and power in the 1370s and 1380s declined steadily after Trần Nghệ Tông's reign (1370–1372). He had ceded the throne in favor of his son Trần Duệ Tông (r. 1372–77), his grandson Trần Phế Đế (r. 1377–88), and Trần Thuận Tông (r. 1388–98), one of his younger sons.
The Trần dynasty became known for emperors who reigned for only a few years before relinquishing the throne to a favorite son, and becoming Thái Thượng Hoàng Đế, the first dynasty to take the name of Father of "Hoàng Đế" emperor title. These types of short-lived and short-sighted emperors encouraged the arrival and ascension of strong, skillful and sly politicians. Hồ Quý Ly was such a politician. He was widely known for his cunning, courage, and boldness, and had distinguished himself in a successful campaign against the Chams of Champa. Through his scheming and shrewd marriage alliances (to a sister of Emperor Trần Duệ Tông and Trần Thuận Tông), Hồ Quý Ly made himself a court fixture in the position of the emperors' indispensable advisor. In less than 20 years, while many others involved in court intrigues were being assassinated all around him, Hồ Quý Ly attained the highest post of General/Protector/Regent of the country in 1399.
Coup d'etat of Hồ Quý Ly (1399)[edit]

Coins issued by Hồ dynasty, Vietnam in the 15th century. They are made from bronze
To facilitate his takeover, Hồ Quý Ly first had a new capital built, called Tây Đô (literally "Western Capital"). In 1399, he invited the current emperor, Trần Thuận Tông, to visit this new capital. After coaxing the emperor into relinquishing the throne to Prince An (a three-year-old child) he had Trần Thuận Tông imprisoned in a pagoda and later executed. Prince An "reigned" for one year until Hồ Quý Ly deposed him in 1400 and declared himself to be the new emperor.
Đại Ngu[edit]
Hồ Quý Ly immediately changed the country's name from Đại Việt to Đại Ngu (大虞, meaning "Great Peace"), which might have been inspired by Hồ Quý Ly's claims that the Hồ family were descendants of Shun of Yu (虞舜, "Ngu" is Vietnamese pronunciation for 虞 "Yu") through Gui Man (媯滿), the Duke Hu of Chen ("Hồ" is the Vietnamese pronunciation for "胡 Hu").[4][5]
Taking a page from the ruling book of his Trần predecessors, Hồ Quý Ly reigned less than a year before relinquishing the throne to his second son, Hồ Hán Thương. He then became known as the Emperor's Highest Father (太上皇, Sino-Vietnamese: Thái thượng hoàng).
Vernacular Vietnamese language written in the Chữ nôm script was promoted by the Hồ over Classical Chinese.
Final years[edit]
In 1402 the army of the Hồ dynasty under general Đỗ Mãn made significant inroads against Champa, prompting the Champa king to cede large territory to Vietnam.[6]

Terracotta Phoenix head used as architectural decoration, from the 14th–15th century

North gate of Tây Đô castle
Hồ Hán Thương, emperor 1401–06[edit]
Foreign diplomacy[edit]
Stable relations with the Ming dynasty were Hồ Quý Ly's foremost concern. Unfortunately, this matter proved impossible for the Hồ to pursue by that time of civil unrest. The descendants of the deposed Trần dynasty had begun agitating against the "usurper" Hồ Quý Ly. This internal disquiet kept the country in chaos and allowed an opportunity for the Ming to conquer Đại Việt with the help of the Trần sympathizers. From 1400 through 1405, the Hồ tried in vain to regain China's goodwill. They sent emissaries and diplomats with offerings to Beijing but the gifts were each time refused or belittled.[citation needed] Hồ Quý Ly (though not an emperor at that time) realized that this stubborn attitude indicated that sooner or later the Ming would invade his country and obligate him to defend it.[citation needed][POV? ]
In May 1403, Hồ Quý Ly's requested the recognition of his son from the Ming court on the account that the Trần lineage had died out and that his son was a royal nephew.[7] Unaware of Hồ's coup, the Yongle Emperor granted him this request.
In October 1404, a Trần Thiên Bính (陳添平) arrived at the Ming court in Nanjing, claiming to be a Trần prince, and appealed to the Yongle Emperor to press his claim to the throne.[8] However, in the 1395 Ancestral injunctions, the Yongle Emperor's father, the Hongwu Emperor, specifically ordered that China should never attack Annam[9] – the Yongle Emperor thus took no action until early 1405, when a Vietnamese envoy confirmed the pretender's story,[8] whereupon he issued an edict reprimanding Hồ Quý Ly and demanding that the Trần be restored.[8][10]
Hồ Quý Ly had doubts about the pretender's claims, but nevertheless agreed to receive the pretender as king.[8][10] Thus, Trần Thiên Bính was escorted back by a military convoy, accompanied by a Ming ambassador.[8] However, on 4 April 1406, as the party crossed the border into Lạng Sơn,[8] Hồ's forces ambushed them and killed both the prince[8] and the Ming ambassador.[11] Hồ also begun harassing the southern border of the Ming.[12]
Defeat and shatter[edit]
On 11 May[8] 1406, the Yongle Emperor sent two forces for an invasion. Zhu Neng, Duke of Chengguo, was appointed Commander-in-Chief, Zhang Fu, Marquis of Xincheng, and Mu Sheng, Marquis of Xiping, were appointed Vice-Generals of the Right and of the Left, respectively. (Zhu died of illness en route and was replaced by Zhang) The Ming Shilu 2 December 1407 entry recorded the Yongle Emperor's order to Marquis Zhang Fu not to harm any innocent Vietnamese.[13] In 1407, the fall of Da Bang fortress, and the defeats of the Hồ at Moc Pham Giang and Ham Tu all precipitated the fall of the Hồ dynasty. At the Ham Tu battle, the Hồ family tried to escape the enemy but was caught by the Ming and sent to exile in China. From 1407 till 1417, the Ming ruled Nanyue[when defined as?] more ruthlessly than ever before.[citation needed][POV? ] It is said[by whom?] the Ming sent valuable treasures such as gems, jade, and golden artworks, as well as many valuable books, back to Beijing.[dubious ] Among these were the National History Books of Vietnam which told of Vietnam's past up to the Trần dynasty. The cruelty[POV? ] and exploitation of the Ming fueled the awakening of the Lam Son Rebellion led by Lê Lợi.[citation needed]
However, after the defeat of the Hồ dynasty by the Ming in 1406, Hồ Quý Ly, his sons Hồ Hán Thương and Hồ Nguyên Trưng, and other relatives were captured and sent to Guangxi. There Hồ Quý Ly was put to work as a Chinese soldier and security guard[dubious ] until the end of his life.
Economy and finance[edit]
Although the leader of the most unpopular and probably the most hated dynasty in the history of Vietnam,[citation needed]Hồ Quý Ly nevertheless initiated many economic, financial and educational reforms. One notable reform for which Hồ is credited was the introduction of the a country-wide paper currency around 1399 or 1400.[14] Other reforms included land reform, opening of ports to foreign trade, reform of the judiciary, health care and opening the education system to study mathematics and agriculture alongside Confucian texts.[15]
See also[edit]
- List of Vietnamese dynasties
- Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty
- Nam Ông mộng lục
References[edit]
^ "Ho Dynasty Citadel becomes world heritage site Archived 2012-07-01 at the Wayback Machine", Tuổi Trẻ, June 28, 2011
^ K. W. Taylor (9 May 2013). A History of the Vietnamese. Cambridge University Press. pp. 166–. ISBN 978-0-521-87586-8..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Kenneth R. Hall (2008). Secondary Cities and Urban Networking in the Indian Ocean Realm, C. 1400-1800. Lexington Books. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-0-7391-2835-0.
^ Trần, Xuân Sinh (2003). Thuyết Trần. p. 403....Quý Ly claims Hồ's ancestor to be Mãn the Duke Hồ [Man, Duke Hu], founding meritorious general of the Chu dynasty, king Ngu Thuấn's [king Shun of Yu] descendant, created his country's name Đại Ngu...
^ Trần, Trọng Kim (1919). "I.III.XI.". Việt Nam sử lược. Vol.I.Quí Ly deposed Thiếu-đế, but respected [the relationship] that he [Thiếu Đế] was his [Quí Ly's] grandson, only demoted him to prince Bảo-ninh 保寧大王, and claimed himself [Quí Ly] the Emperor, changing his surname to Hồ 胡. Originally the surname Hồ [胡 Hu] were descendants of the surname Ngu [虞 Yu] in China, so Quí Ly created a new name for his country Đại-ngu 大虞.
^ Andrew David Hardy, Mauro Cucarzi, Patrizia Zolese Champa and the Archaeology of Mỹ Sơn (Vietnam) 2009 Page 68 "In 1402, the Hồ dynasty sent General Đỗ Mãn to lead the army against Champa."
^ Chan 1990, 229.
^ abcdefgh Chan 1990, 230.
^ Mote, Frederick W.; Twitchett, Denis; Fairbank, John K., eds. (1988). The Cambridge History of China: Volume 7, The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644. Contributors Denis Twitchett, John K. Fairbank (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 229. ISBN 0521243327. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
^ ab Dreyer 1982, 207–208.
^ Tsai 2001, 179.
^ Tsai 2001, 181.
^ "Southeast Asia in the Ming Shi-lu: an open access resource". Geoff Wade, translator. Singapore: Asia Research Institute and the Singapore E-Press, National University of Singapore. p. 1014. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
^ Anh Tuấn Hoàng Silk for Silver: Dutch-Vietnamese Relations, 1637–1700 2007 – Page 133 "There was a brief period during the Hồ dynasty (1400–07) when paper money was introduced."
^ Jan Dodd, Mark Lewis, Ron Emmons The Rough Guide to Vietnam 4th Edition 2003– Page 486 "Though the Ho dynasty lasted only seven years, its two progressive monarchs launched a number of important reforms. They tackled the problem of land shortages by restricting the size of holdings and then rented out the excess to landless peasants, the tax system was revised and paper money replaced coinage, ports were opened to foreign trade, the judiciary was overhauled and public health care introduced. Even the education system came under review and was broadened to include mathematics, agriculture and other practical subjects along with the classic Confucian texts."
Sources[edit]
- Hall, Kenneth R., ed. (2008). Secondary Cities and Urban Networking in the Indian Ocean Realm, C. 1400–1800. Volume 1 of Comparative urban studies. Lexington Books.
ISBN 0739128353. Retrieved 7 August 2013. - Taylor, K. W. (2013). A History of the Vietnamese (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press.
ISBN 0521875862. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
Viet Nam Toan Thu, by Pham Van Son
Viet Nam Su Luoc, by Trần Trọng Kim
Chan, Hok-lam (1990). "The Chien-wen, Yung-lo, Hung-hsi, and Hsüan-te reigns, 1399-1435". The Cambridge History of China. Volume 7: The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644 (Part 1). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24332-7.
Dardess, John W. (2012). Ming China, 1368-1644: A concise history of a resilient empire. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-0491-1.
Dreyer, Edward L. (1982). Early Ming China: A political history, 1355-1435. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-1105-4.
Shiro, Momoki (2004). "Great Viet". Southeast Asia. Santa Barbara: ABC Clio. ISBN 9781576077702.
Tsai, Shih-shan Henry (2001). Perpetual happiness: The Ming emperor Yongle. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-98109-1.
| Preceded by Trần dynasty | Dynasty of Vietnam 1400–1407 | Succeeded by Fourth Chinese domination/Posterior Trần dynasty |
Categories:
- 1407 disestablishments in Asia
- 15th-century disestablishments in Vietnam
- Vietnamese dynasties
- States and territories established in 1400
- 1400 establishments in Asia
- 15th-century establishments in Vietnam
- People of Zhejiang descent
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.892","walltime":"1.066","ppvisitednodes":{"value":5459,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":72165,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":10717,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":16,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":6,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":37742,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":0,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 969.860 1 -total"," 54.83% 531.771 1 Template:Infobox_Former_Country"," 49.38% 478.879 3 Template:Infobox"," 20.65% 200.230 3 Template:Lang"," 15.29% 148.322 1 Template:Reflist"," 12.64% 122.549 1 Template:ISO_3166_code"," 12.11% 117.440 10 Template:Cite_book"," 8.86% 85.886 3 Template:Citation_needed_span"," 7.81% 75.751 3 Template:Fix-span"," 7.30% 70.817 9 Template:Fix"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.533","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":16684264,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1320","timestamp":"20190121193427","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Hu1ed3 dynasty","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H%E1%BB%93_dynasty","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1209047","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1209047","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2005-11-30T22:42:13Z","dateModified":"2018-11-01T15:45:55Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/04/Map_of_the_Tr%E1%BA%A7n_dynasty_%281225-1400%29.png","headline":"dynasty"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":108,"wgHostname":"mw1272"});});